A strong foundation is essential for success in the ever changing fields of project management and technological innovation. One of the most fundamental tools for this foundation is the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). This article will explore the traditional approach to WBS, as defined by the Project Management Institute (PMI), and contrast it with our innovative methodology at Genialprojects. By understanding both perspectives, project managers, product managers, and organizational leaders can gain insights into constructing an effective WBS that enhances project planning and execution.
What is a Work Breakdown Structure?
According to the PMI's Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK v6), a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team. The WBS organizes and defines the total scope of the project and breaks it down into manageable sections or tasks. This decomposition ensures that each component of the project scope is clearly defined and easier to manage.
The WBS serves as a comprehensive guide for project teams, transforming the project scope statement into a detailed plan. By breaking down the project into smaller, more manageable pieces, teams can focus on specific tasks, ensuring nothing is overlooked. This structured approach not only enhances clarity but also facilitates better resource allocation, time management, and risk assessment.
Key Elements of a WBS
A well-constructed WBS is composed of several key elements that form a structured hierarchy:
- Project Name: At the top level, the project name defines the overall initiative. This level represents the ultimate goal and scope of the project.
- Phases: The second level typically consists of major phases or deliverables of the project. Each phase represents a significant component of the project’s lifecycle.
- Work Packages: Below the phases are work packages, which are more granular tasks or groups of activities. These packages represent units of work that can be assigned, scheduled, and tracked.
- WBS Dictionary: The WBS dictionary is a companion document that provides detailed information about each element in the WBS. It includes definitions, scope, responsibilities, and other pertinent details that support the WBS.
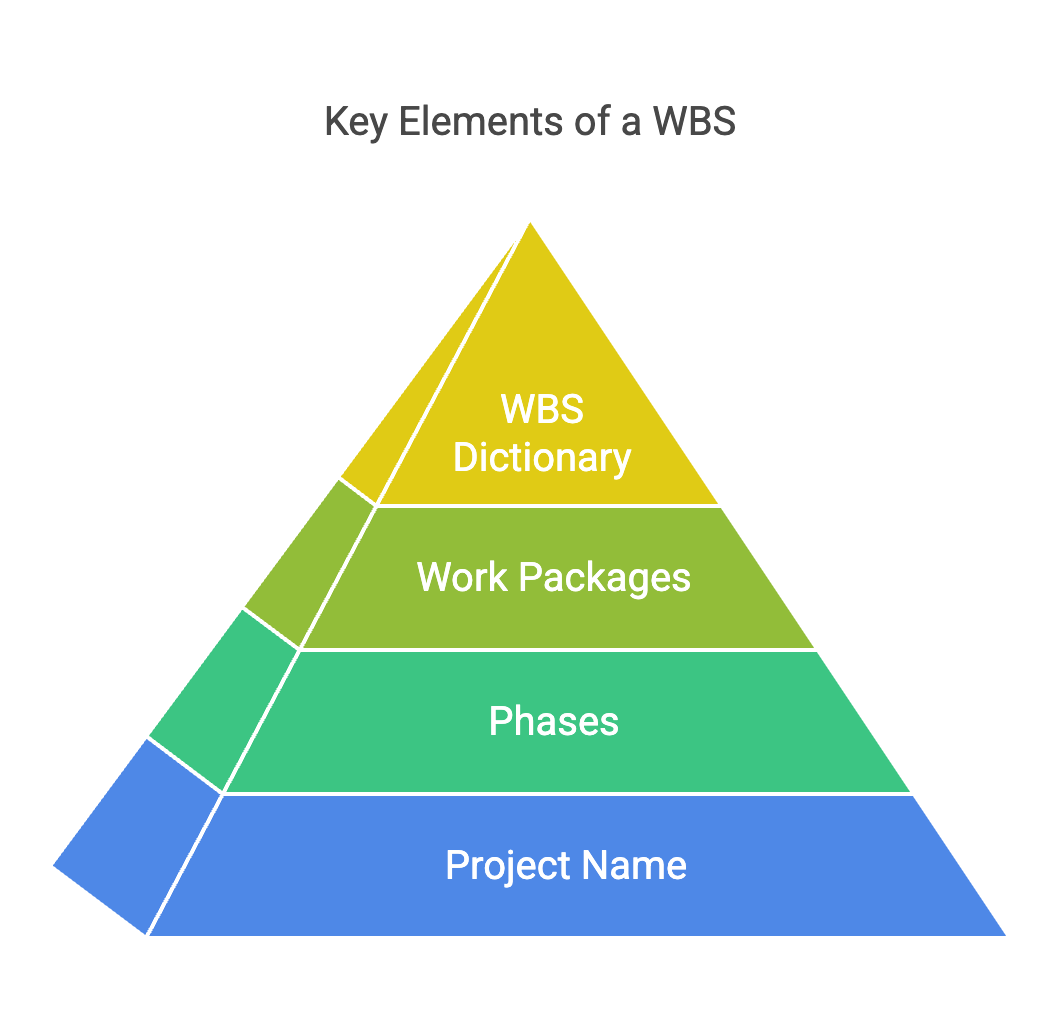
Each level of the WBS provides a greater degree of detail, ensuring that every aspect of the project is accounted for and meticulously planned.
When to Use a WBS?
As recommended by the PMI, the WBS should be developed during the project planning phase, immediately following the creation of the project scope statement. This timing allows for a thorough understanding of the project’s objectives and deliverables before breaking them down into detailed tasks.
While the WBS is traditionally associated with waterfall methodologies, it is equally beneficial in agile and hybrid frameworks. In agile environments, the WBS can be aligned with iterations and sprints, breaking down the scope into user stories and tasks. This flexibility makes the WBS a versatile tool for any project management approach, facilitating clear communication and efficient task management across various methodologies.
Our Approach to WBSs
At Genialprojects, we advocate for a slightly modified approach to constructing a WBS. We believe this adaptation enhances its practicality and effectiveness in today’s dynamic project environments. Our approach begins with identifying the key milestones of the project, which we place at the second level of the WBS hierarchy, rather than traditional phases.
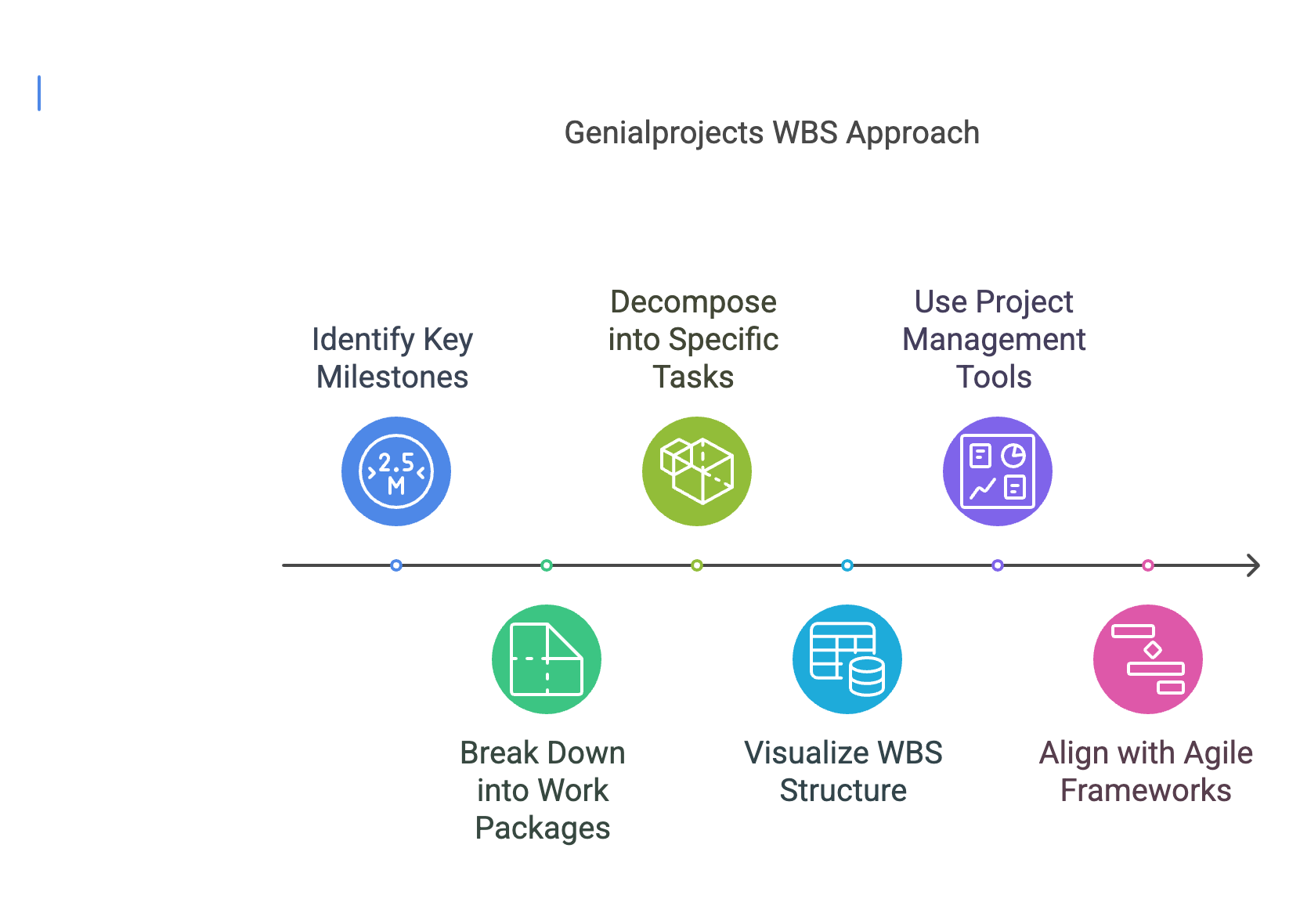
- Milestones as Level Two: By focusing on major project milestones, we ensure that significant achievements and checkpoints are highlighted. This milestone-centric approach allows for better tracking of progress and critical deliverables.
- Work Packages and Tasks: Each milestone is further broken down into work packages (Level Three). These packages represent substantial units of work necessary to achieve each milestone. Subsequently, each work package is decomposed into specific tasks (Level Four), detailing the individual actions required.
- Visualization and Tools: For enhanced clarity, the first three levels of the WBS can be visualized on a single page. This provides a clear, high-level view of the project structure. For detailed task management at Level Four, we recommend using project management software or spreadsheets. By utilizing project management tools from the outset, planning becomes more efficient and adjustments more manageable.
- Agile Alignment: This structured yet flexible approach is particularly advantageous in agile frameworks, where work packages can be mapped directly to user stories. This parallel structure facilitates smoother transitions between planning and execution phases, ensuring that agile teams can maintain their iterative cycles without losing sight of the overall project scope.
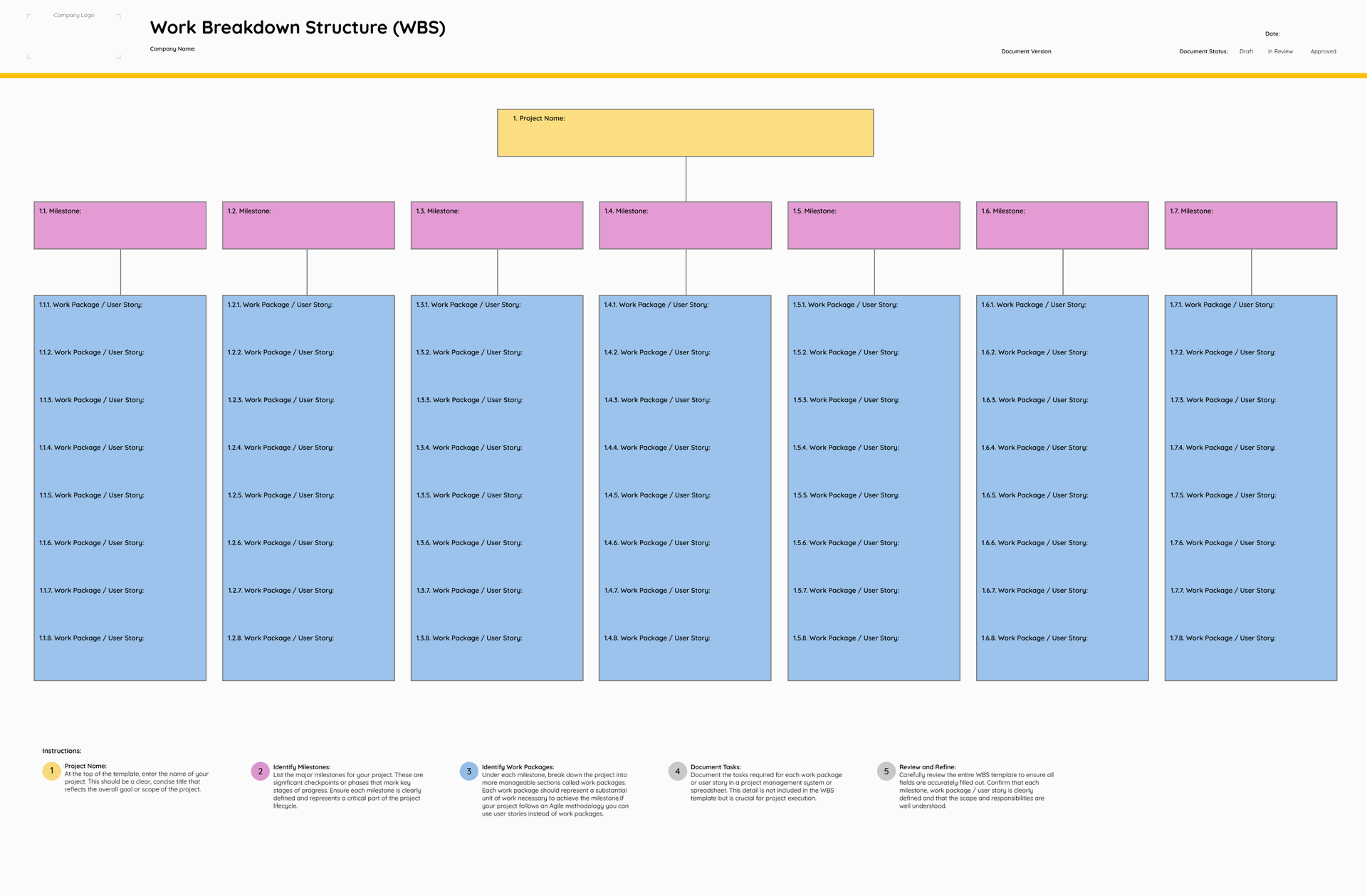
Free Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Template available on our website.
Key Takeaways
Understanding and implementing an effective Work Breakdown Structure is crucial for the successful management of any project. The traditional WBS, as defined by PMI, provides a robust framework for breaking down project scope into manageable tasks. However, at Genialprojects, we advocate for a milestone-centric approach that enhances clarity and aligns well with both traditional and agile methodologies.
By focusing on milestones, breaking down work packages, and utilizing project management tools, our approach ensures that every aspect of the project is meticulously planned and easily trackable. This methodology not only streamlines project management processes but also fosters better communication and coordination among team members.
In conclusion, adopting a flexible and detailed WBS approach tailored to your project's specific needs can significantly improve project planning and execution. Whether you are managing a traditional project or an agile initiative, the principles of a well-constructed WBS remain a cornerstone of effective project management.