In the ever-accelerating landscape of technology and business, a new force is reshaping how work gets done: artificial intelligence. For many, the advent of AI in the workplace conjures images of robotic overlords replacing human jobs. However, for the field of project management, the reality is far more nuanced and exciting. Instead of a replacement, AI is emerging as a powerful co-pilot, fundamentally transforming the role of the project professional from a tactical taskmaster to a strategic leader.
This article explores the evolution of this crucial discipline, charts the rise of AI as a transformative force, and introduces a proprietary framework designed to help organizations—and the individuals who lead them—harness this synergy to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, foresight, and strategic value.
The Evolution of Project Management
The practice of project management has a rich and storied history, evolving from simple methodologies to highly sophisticated, data-driven disciplines. Its legacy is one of continuous adaptation. From the early days of constructing pyramids to the intricate logistics of the Apollo missions, the core challenge has always been to deliver complex outcomes within constraints.
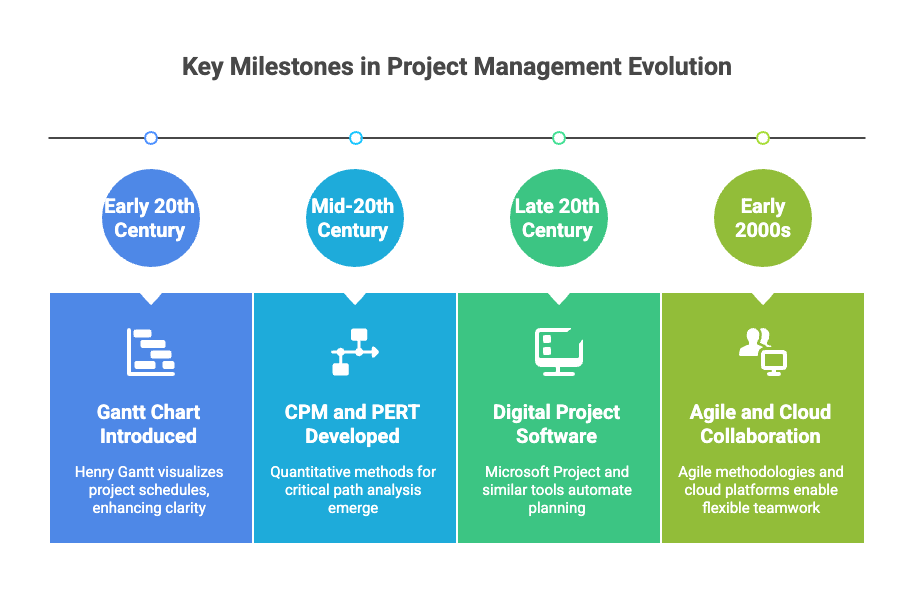
The journey began with foundational tools like the Gantt Chart, a visual representation of a schedule introduced by Henry Gantt in the early 20th century. This innovation brought a new level of clarity and control to complex work. The mid-20th century saw the development of more sophisticated methods like CPM (Critical Path Method) and PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique), which introduced quantitative analysis to identify the longest path of dependent tasks, a crucial step for managing large-scale, complex initiatives. These methodologies laid the groundwork for modern project software.
The digital revolution of the late 20th century brought these tools to the desktop, with software like Microsoft Project becoming the standard. The rise of the internet and agile methodologies in the early 2000s shifted the focus from rigid planning to flexible, iterative execution. Cloud-based platforms like Jira and Trello made collaboration fluid and real-time. This iterative evolution, driven by the need for speed and adaptability, set the stage for the next great paradigm shift: the infusion of AI.
A Timeline of AI Milestones
The integration of artificial intelligence into the business world has been a gradual process, but its application in project delivery has a more recent and rapid trajectory.
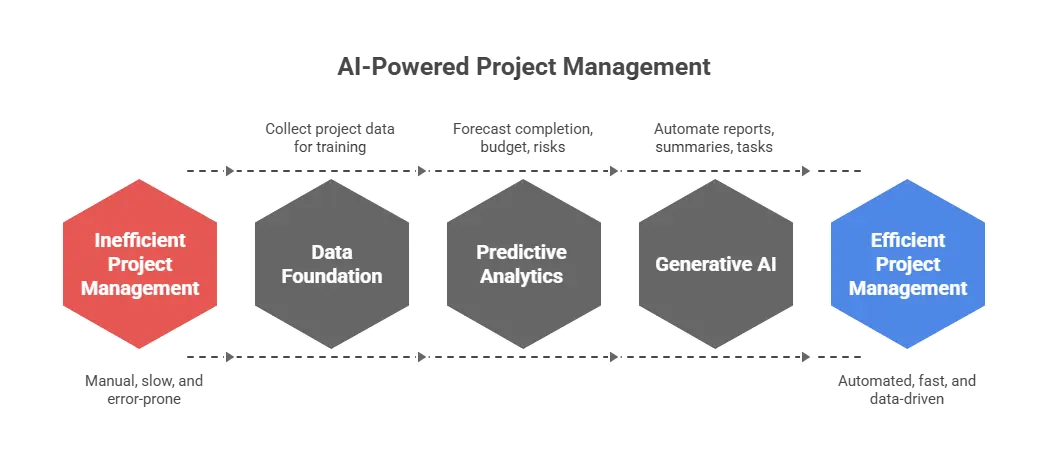
- Early 2000s -The Data Foundation: The rise of big data and cloud computing provided the necessary infrastructure. Organizations began collecting vast amounts of data on their initiatives, from task completion times to budget deviations, creating the datasets that would eventually train machine learning models.
- Late 2010s - The Dawn of Predictive Analytics: AI's first major foray into project management came in the form of predictive analytics. Algorithms trained on historical project data could now forecast task completion times, predict budget overruns, and even identify the probability of risks—a significant leap from traditional deterministic models.
- Early 2020s - Generative AI and Automation: The breakthrough of Generative AI with models like GPT marked a new inflection point. This technology introduced capabilities such as automatic report generation, dynamic meeting summaries, and even autonomous task creation, bringing true intelligent automation to the field.
The convergence of these two distinct timelines—the legacy of project management and the advancements in AI—is creating a new operating model. This convergence is not merely about a new feature set; it's about fundamentally redefining how projects are planned, executed, and governed.
Current State: Challenges and Opportunities
The current state of AI in project management is a mix of immense opportunity and significant challenges. While the potential for increased efficiency and strategic insight is clear, many organizations are still in the early stages of adoption.
A primary challenge is data quality and governance. AI models are only as good as the data they're trained on. Inconsistent, incomplete, or siloed data can lead to biased or inaccurate predictions, undermining the trust of the project team. Another hurdle is the skill gap. Project professionals often lack the data literacy to fully leverage AI tools, and a general fear of job displacement can create resistance to adoption. Furthermore, the ethical considerations of AI, such as algorithmic bias and the transparency of decision-making, are increasingly important issues that need to be addressed.
However, the opportunities far outweigh the challenges. The most significant opportunity is the ability to free up human capital. By automating routine, administrative tasks, AI allows project professionals to focus on higher-value activities like stakeholder engagement, strategic problem-solving, and team coaching. AI also provides a new level of predictive foresight, allowing teams to shift from a reactive to a proactive stance, addressing potential issues before they become crises. This new dynamic transforms the practice from a series of reactive corrections to a continuous process of intelligent optimization.
Core AI Functional Areas in Project Management
AI's impact can be categorized into several core functional areas, each contributing to a more intelligent and efficient approach to initiative delivery.
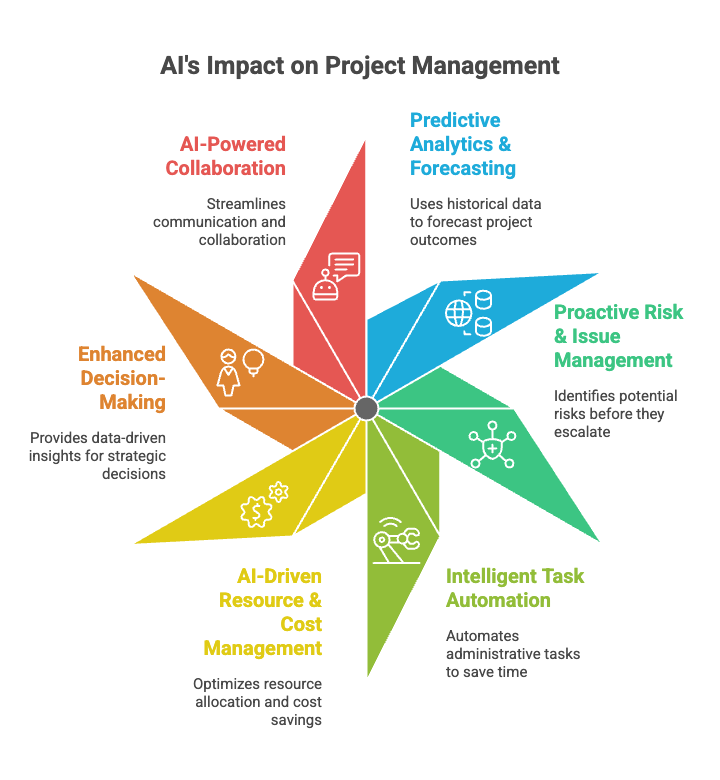
Predictive Analytics & Forecasting
This is perhaps the most mature application of AI in the field. Algorithms analyze historical data—including past performance, resource allocation, and external market factors—to forecast completion dates, budget needs, and potential schedule deviations with a high degree of accuracy. This enables leaders to make proactive adjustments rather than reacting to a project that's already off track.
Proactive Risk & Issue Management
AI models can scan project documentation, communication logs, and external news feeds to identify potential risks long before they surface. By recognizing patterns and anomalies, the system can flag potential issues, such as a team member's workload becoming a risk factor or a change in market conditions affecting a key deliverable.
Intelligent Task Automation & Workflow Optimization
AI can automate a wide range of administrative tasks. From generating meeting minutes and assigning action items to creating initial project plans and status reports, automation frees up significant time for the team. AI-driven workflow optimization can also identify bottlenecks and suggest more efficient processes based on historical data.
AI-Driven Resource & Cost Management
Managing resources and budgets is often one of the most complex aspects of a large-scale program. AI can optimize resource allocation by matching skills to tasks, forecasting resource needs, and identifying cost-saving opportunities by analyzing spending patterns.
Enhanced Decision-Making & Strategic Insights
AI provides data-driven insights that go beyond simple reporting. By analyzing complex datasets, AI can help executives and team leaders understand the "why" behind project performance, identify root causes of delays, and provide strategic recommendations for course correction.
AI-Powered Collaboration & Communication
AI assistants and chatbots can streamline communication by answering frequently asked questions, summarizing long email threads, and even facilitating cross-functional collaboration by providing context from other departments.
The Human-AI Partnership & Ethical Governance
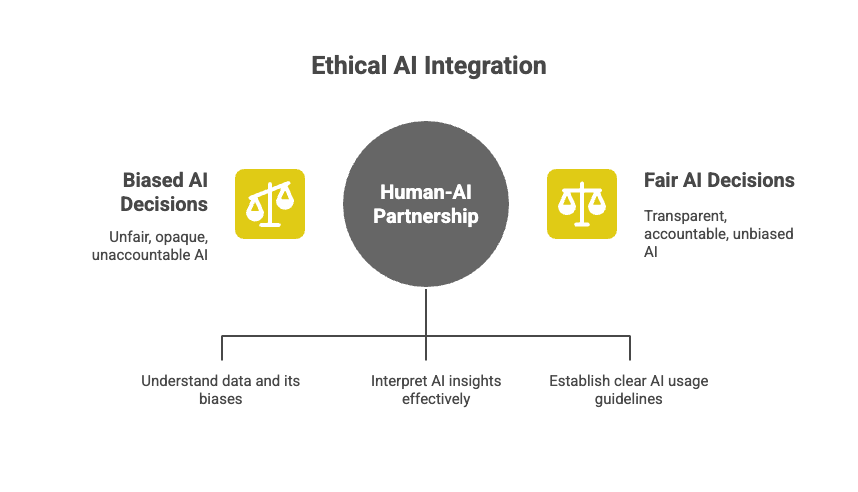
The successful integration of AI is not about replacing human judgment; it's about creating a powerful human-AI partnership. The project professional remains the final decision-maker, using their experience, emotional intelligence, and strategic acumen to interpret and act on AI's insights. This partnership requires a new set of skills, including data literacy, critical thinking, and a deeper understanding of the ethical implications of using AI.
Ethical governance is a non-negotiable component of this partnership. Organizations must establish clear guidelines for how AI is used, ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability. This includes actively monitoring for algorithmic bias, ensuring the data used is representative and unbiased, and providing a clear explanation of how the AI arrived at its conclusions.
The New PM Superpowers: Where AI Is Making an Impact
AI isn't just changing tools; it's changing the very nature of what it means to be a project professional, granting them new "superpowers."
- Beyond Automation: Freeing PMs for Strategic Work. The single greatest gift of AI is time. By automating the mundane, repetitive work of scheduling, tracking, and reporting, AI liberates project professionals to focus on the truly strategic aspects of their role. This includes managing stakeholders, mentoring team members, and proactively navigating political and organizational complexities.
- From Gut Instinct to Data-Driven Decisions. For decades, many project decisions relied on a manager's experience and intuition. While valuable, this gut instinct can be fallible. AI provides a new level of objective, data-driven foresight. It transforms the project leader from a reactive troubleshooter to a proactive strategist, armed with quantifiable evidence to support every critical decision.
- The Shift from Task Manager to Strategic Leader. As AI takes on the administrative burden, the role of the project professional elevates. The focus shifts from checking off tasks on a list to ensuring the initiative delivers genuine strategic value to the organization. This new paradigm positions the project professional not just as a manager of tasks, but as a business partner and catalyst for innovation.
Top-Tier AI-Powered Project Management Tools
The market for AI-powered project management tools is rapidly maturing, with a few key players leading the charge.
- ClickUp: Positioning itself as "one app to replace them all," ClickUp's AI capabilities are deeply integrated into its platform. "ClickUp Brain" acts as a personal AI assistant, capable of generating summaries, creating content, and even assisting with project planning.
- Monday.com: Known for its highly customizable dashboards, Monday leverages AI for intelligent automation. Its AI-powered features include automating routine tasks, providing predictive insights on workload distribution, and generating reports.
- Asana: A pioneer in work management, Asana's AI features focus on enhancing efficiency. The tool offers intelligent task prioritization, automatic workflow setup, and a smart inbox that helps professionals focus on what matters most.
- PMI Infinity: Developed by the Project Management Institute (PMI), this platform aims to be a comprehensive ecosystem for the modern project professional. While still in its early stages, it is being built with native AI at its core to provide data-driven insights and a personalized experience.
- Wrike: With its "Wrike Work Intelligence" platform, this tool provides AI-driven analytics, risk identification, and content generation. Its strength lies in its ability to handle complex, enterprise-level initiatives.
- Linear: A tool favored by product and engineering teams, Linear uses AI to streamline bug tracking and feature development. Its AI helps categorize issues, prioritize backlogs, and provide a clear overview of a project's health.
Tool Name | Primary AI Strength | Key AI Features | Best For |
ClickUp | AI Knowledge Management & Automation | Generates summaries, creates content, assists with planning, autamates tasks. | All-in-one work management, internal knowledge bases, team collaboration. |
| Monday.com | Intelligent Workflow Automation | Automates routine tasks, provides predictive insights on workload, generates reports, customizable dashboards. | Flexible, highly customized project workflows, cross-functional teams. |
Asana | Enhanced Task Prioritization & Efficiency | Intelligent task prioritization, automatic workflow setup, smart inbox for focus. | Teams needing streamlined task management, workflow automation, and focused work. |
PMI Infinity | AI-Powered Project Coaching & Guidance | Provides prompt libraries, guided experiences, document generation, and a knowledge base of vetted content. | Project professionals seeking tactical assistance, skill enhancement, and best practices. |
Wrike | Predictive Risk & Work Intelligence | AI-driven analytics, predictive risk identification, content generation for project documentation, workflow automation. | Complex, enterprise-level initiatives, projects with high risk components. |
Linear | Streamlined Development Workflow | AI-powered bug categorization, backlog prioritization, project health overview. | Product and engineering teams focused on software development and issue tracking. |
The Frameworks Shaping the Conversation
As AI's role in project delivery grows, so too do the frameworks designed to guide its implementation. Here's a look at some of the most influential approaches from top consultancies and standardization bodies.
The PMI Cognitive Project Management in AI (CPMAI)™ Methodology
This methodology, developed by the Project Management Institute, is a landmark effort to provide a structured, data-centric approach to AI-enabled projects. Its philosophy is to combine project management principles with the iterative nature of data science. The CPMAI methodology has six key phases that guide the entire process: Business Understanding, Data Understanding, Data Preparation, Model Development, Model Evaluation, and Model Operationalization. Its primary focus is on ensuring AI initiatives are managed with the same rigor and discipline as traditional projects.
The McKinsey AI Strategy Framework
McKinsey's approach is not a rigid methodology but a strategic framework for C-level executives. The core philosophy centers on a five-step journey to AI-driven transformation: defining the AI strategy, identifying use cases, building the foundation (data, talent, tech), scaling solutions, and managing change. McKinsey's framework is primarily focused on aligning AI adoption with broader business objectives and cultural transformation.
The Deloitte AI Adoption Journey
Deloitte's framework is designed to help organizations at different levels of AI maturity. It breaks down the adoption journey into a series of steps: Strategy, Foundation, Scale, and Realization. Its core philosophy is to create a holistic AI ecosystem that includes technology, talent, and data governance. The primary focus is on a phased approach to de-risk implementation and ensure the value of AI is fully realized.
Framework Name | Primary Audience | Core Philosophy | Key Stages/Roles | Primary Focus |
PMI CPMAI™ | Project & Program Managers | Data-centric, iterative project management | 6 Phases: From Data Prep to Model Ops | AI initiative delivery |
McKinsey AI Strategy | C-Level, Executives | Business & cultural transformation through AI | 5-Step Journey | Business value & strategic alignment |
Deloitte AI Adoption | Business Leaders, PMO | Phased, holistic AI ecosystem build | 4 Stages: Strategy to Realization | De-risked implementation & value realization |
Introducing the Genialprojects Agile Intelligence Framework™ (AIF)
Drawing from the best practices of industry leaders and the pressing needs of our clients, Genialprojects is proud to introduce our proprietary Agile Intelligence Framework™ (AIF). The AIF is a unique, three-pillar framework designed to provide a clear, actionable roadmap for organizations seeking to integrate AI into their project delivery.
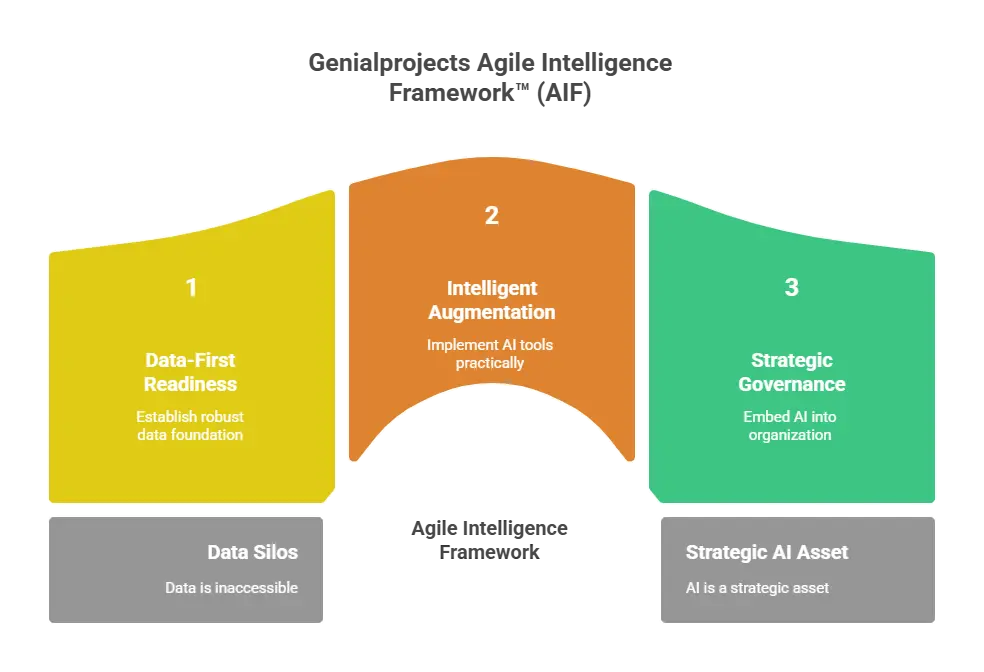
Pillar 1: The Foundation - Data-First Readiness
Before any AI model can be deployed, a robust data foundation must be established. This pillar focuses on helping organizations move beyond data silos to create a unified, clean, and accessible data ecosystem.
- Objective: To establish a secure, high-quality data foundation that can effectively train and sustain AI models.
- Key Activities: Data governance policy design, data quality audits, establishing data pipelines, and a knowledge management system.
- Deliverables: Data Readiness Assessment, AI Data Strategy Roadmap, Clean & Tagged Datasets.
Pillar 2: The Engine - Intelligent Augmentation
This pillar is about the practical implementation of AI tools and methodologies. It moves beyond theoretical discussions to a hands-on approach, augmenting existing workflows with intelligent tools.
- Objective: To strategically integrate AI tools to automate tasks, provide predictive insights, and augment team performance.
- Key Activities: AI use-case identification (e.g., predictive scheduling), pilot project implementation, tool selection and integration, and team training.
- Deliverables: AI Integration Plan, Pilot Project Report, Augmented Workflows & Dashboards.
Pillar 3: The Advantage - Strategic Governance
The final pillar ensures that AI is not just a tactical tool but a strategic asset. It focuses on embedding AI into the organization's culture and governance structure, ensuring continuous improvement and ethical oversight.
- Objective: To create a sustainable, data-driven culture and governance model that maximizes AI's strategic value while mitigating risk.
- Key Activities: Establishing an AI Governance Council, developing ethical guidelines, ongoing model validation and monitoring, and defining AI-powered KPIs.
- Deliverables: AI Governance Policy, Strategic Impact Report, Continuous Improvement Loop.
Pillar | Objective | Key Activities | Deliverables |
Pillar 1: The Foundation - Data-First Readiness | To establish a secure, high-quality data foundation that can effectively train and sustain AI models. | Data governance policy design, data quality audits, establishing data pipelines, and a knowledge management system. | Data Readiness Assessment, AI Data Strategy Roadmap, Clean & Tagged Datasets. |
Pillar 2: The Engine - Intelligent Augmentation | To strategically integrate AI tools to automate tasks, provide predictive insights, and augment team performance. | AI use-case identification, pilot project implementation, tool selection and integration, and team training. | AI Integration Plan, Pilot Project Report, Augmented Workflows & Dashboards. |
Pillar 3: The Advantage - Strategic Governance | To create a sustainable, data-driven culture and governance model that maximizes AI's strategic value while mitigating risk. | Establishing an AI Governance Council, developing ethical guidelines, ongoing model validation and monitoring, and defining AI-powered KPIs. | AI Governance Policy, Strategic Impact Report, Continuous Improvement Loop. |
Are you an AI-ready project manager? Free Self-Assessment
¿Eres un Gerente de Proyectos preparado para la IA? Autoevaluación gratuita
Key Takeaways
The role of the project professional is not shrinking; it is evolving. AI is not a replacement but an amplifier, empowering individuals to move beyond the tactical and into the strategic. By embracing a data-first mindset, augmenting workflows with intelligent tools, and establishing a robust governance framework, organizations can transform their project delivery model. The Genialprojects Agile Intelligence Framework (AIF) provides a clear and defensible path forward, positioning our clients at the forefront of this new era.