Creating an effective project budget is a critical skill for any project manager. A well-crafted budget ensures that the project stays on track financially and provides a clear framework for managing resources. This article aims to demystify the process of budgeting, offering practical insights and techniques to make the task straightforward and efficient. At Genialprojects, we understand the importance of a robust project budget and have developed a template to simplify the budgeting process, ensuring your project’s financial success.
What is a Project Budget?
According to the Project Management Institute (PMI), a project budget is a detailed estimate of all the costs required to complete a project within its defined scope and time frame. It is an essential component of the Cost Management Plan and serves as a financial roadmap for project managers. Regardless of the project management framework employed, every initiative and organization can benefit from a well-prepared project budget.
A project budget encompasses all expenses, from labor and materials to contingency reserves and management reserves. In the early stages of a project, such as during the feasibility study, the estimate is more general and the budget may change. However, once funds are authorized and the project begins, there should not be significant changes to the project budget. If changes do occur, they should go through a change control mechanism for approval.
Types of Project Budgets / Details | Raw Order of Magnitude | Budget Estimate | Definitive Estimate |
Main Use | Feasibility study, Project screening, forecasting. | Partial or full funding authorization. | Full funding authorization, bids, proposals, and change orders. |
Accuracy Level | -25% to +75% | -10% to +25% | -5% to +10% |
Estimation Technique | Analogous, Parametric | Parametric, Bottom-up | Bottom-up, Parametric |
Key Elements of a Project Budget
Every project budget should include several essential components to ensure comprehensive financial planning and effective management. Below are the key elements that should be part of any well-structured project budget:
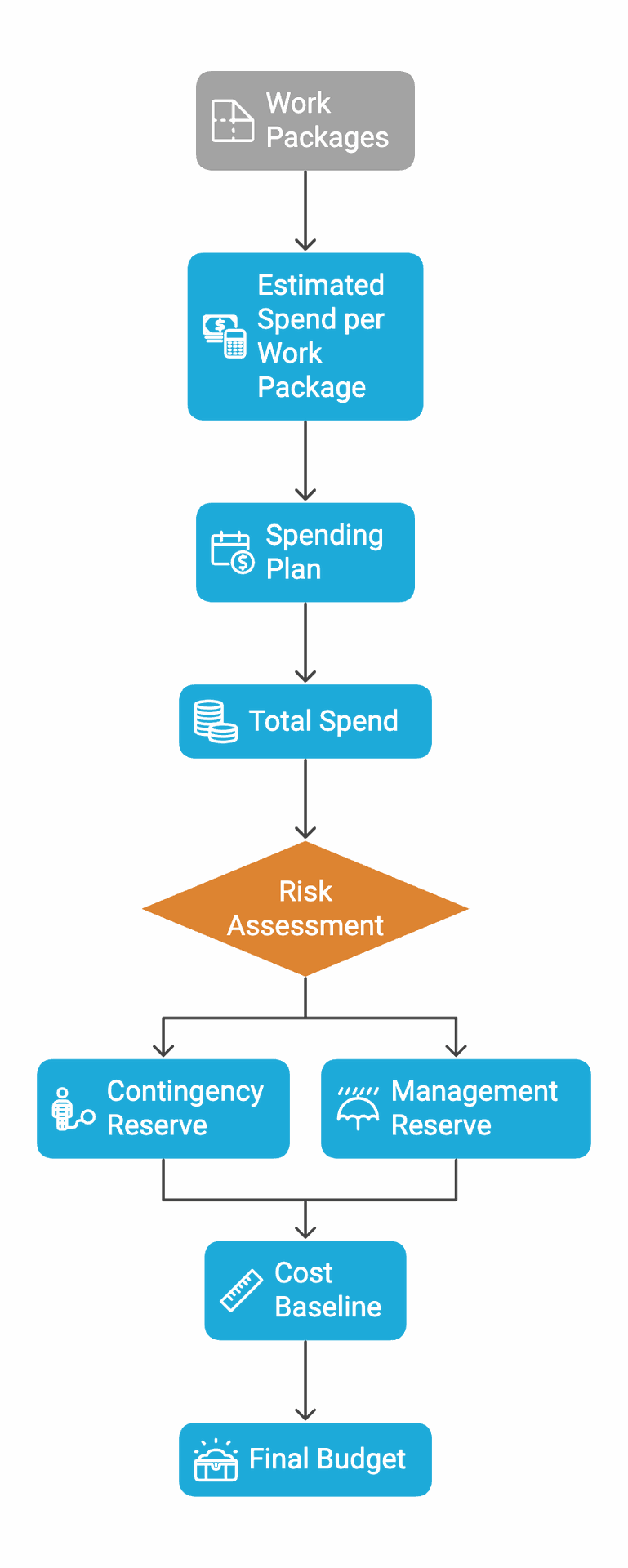
Work Packages
The foundation of any project budget is a well-defined Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). Work packages represent the smallest units of work that need to be accomplished to deliver the project’s objectives. Clearly defining these packages ensures that every aspect of the project is accounted for in the budget.
Estimated Spend per Work Package
Once the work packages are identified, the next step is to estimate the cost associated with each. This includes labor costs, material costs, and any other expenses necessary to complete the tasks. Accurate cost estimation for each work package is crucial for developing a realistic budget.
Spending Plan
A spending plan outlines when the expenditures for each work package will occur throughout the project’s duration. This helps in forecasting cash flow and ensures that funds are available when needed. It is vital to align the spending plan with the project schedule to avoid any financial bottlenecks.
Total Spend
The total spend is the sum of all estimated costs for each work package. This figure represents the initial budget required to complete the project. However, this is just the baseline and does not account for potential risks and uncertainties.
Contingency Reserve
To manage project risks, it is essential to allocate a contingency reserve. This reserve accounts for known risks that might impact the project. At Genialprojects, we recommend setting aside 5% to 15% of the total spend for low-risk projects and 15% to 25% for moderate to high-risk projects.
Cost Baseline
The cost baseline is the sum of the total spend and the contingency reserve. It serves as a benchmark for measuring and controlling cost performance throughout the project. The cost baseline is a critical component of the Cost Management Plan.
Management Reserve
In addition to the contingency reserve, a management reserve is set aside to address unknown unknowns or unforeseen expenses. At Genialprojects, we recommend allocating a management reserve of 5% to 10%. This reserve is not included in the cost baseline but is part of the overall budget.
Final Budget
The final budget is the sum of the cost baseline and the management reserve. It represents the total financial commitment required to deliver the project successfully. Having a comprehensive final budget helps in securing funding and provides confidence to stakeholders.
Cost Estimation
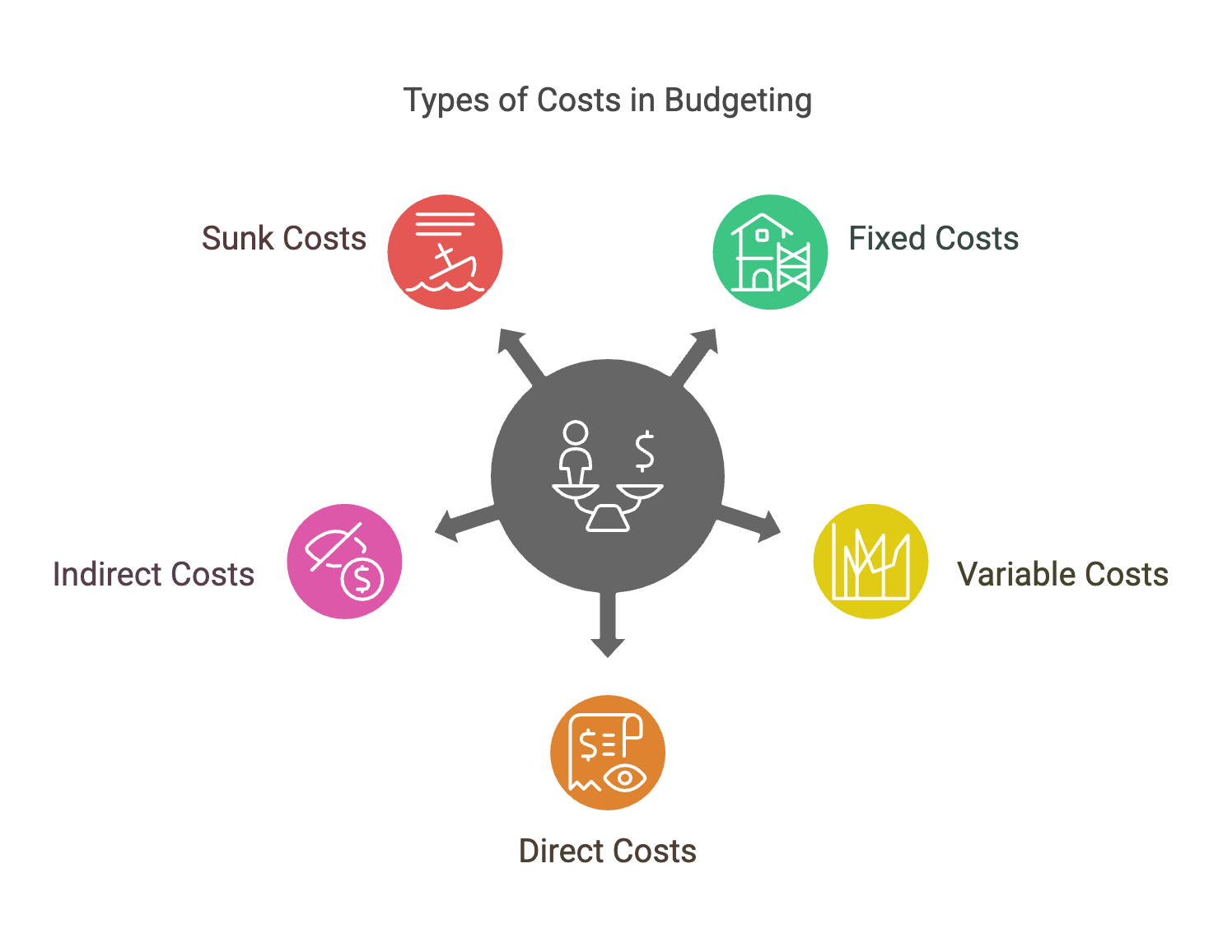
Types of Costs
Understanding the different types of costs is fundamental to accurate budgeting. Now, what types of costs should we consider when estimating the expenditure for a work package? These include:
Fixed Costs: Costs that do not change with the level of production or activity (e.g., rent, salaries).
Variable Costs: Costs that vary directly with the level of production or activity (e.g., raw materials).
Direct Costs: Costs that can be directly attributed to a specific project (e.g., labor, equipment).
Indirect Costs: Costs that are not directly traceable to a specific project (e.g., administrative expenses).
Sunk Costs: Costs that have already been incurred and cannot be recovered (e.g., research and development).
Estimation Techniques
In this section, we mention three popular techniques for estimating project costs:
Analogous Estimating: This technique involves using historical data from similar projects to estimate costs. It is a quick method and is often used in the early stages of a project when limited information is available. However, it is less accurate compared to other techniques because it relies on the assumption that past project costs are a reliable predictor of future project costs.
Parametric Estimating: This method uses statistical relationships and mathematical models to estimate costs based on historical data and other relevant variables. By identifying the key cost drivers and applying these parameters to the current project, parametric estimating can provide a higher level of accuracy. For example, if the cost per unit of output is known, this can be multiplied by the expected output to estimate the total cost. This technique is particularly useful for projects with quantifiable and consistent relationships between cost and project parameters.
Bottom-Up Estimating: This technique involves estimating costs for individual work items and then aggregating them to determine the total project cost. It requires a well-done breakdown of the work needed and is highly accurate because it considers the specific details of each task. However, it is also time-consuming and resource-intensive, as it involves a comprehensive analysis of every component of the project.

In conclusion, selecting the appropriate cost estimation technique depends on the project's phase, the available information, and the desired accuracy. Analogous estimating offers a quick and broad estimate, parametric estimating provides a balance of accuracy and efficiency using statistical models, and bottom-up estimating delivers the highest accuracy through detailed analysis.
When to Use a Project Budget?
It is important to prepare different accuracy levels of project budgets depending on the situation. This ensures that the financial planning is appropriate for the specific phase of the project and its requirements. The following subsections highlight when to use different levels of budget accuracy:
Raw Order of Magnitude
A Raw Order of Magnitude (ROM) estimate is used during the feasibility study and project screening phases. It provides a rough approximation of the project’s cost, typically with a range of -25% to +75%.
Budget Estimates
Budget estimates are more refined than ROM estimates and are used for budgeting and forecasting. They provide a cost estimate with a narrower range of -10% to +25% and are often used for partial or full funding authorization.
Definitive Estimates
Definitive estimates offer the highest level of accuracy, with a range of -5% to +10%. They are used for full funding authorization, bids, proposals, and change orders, ensuring precise cost control.
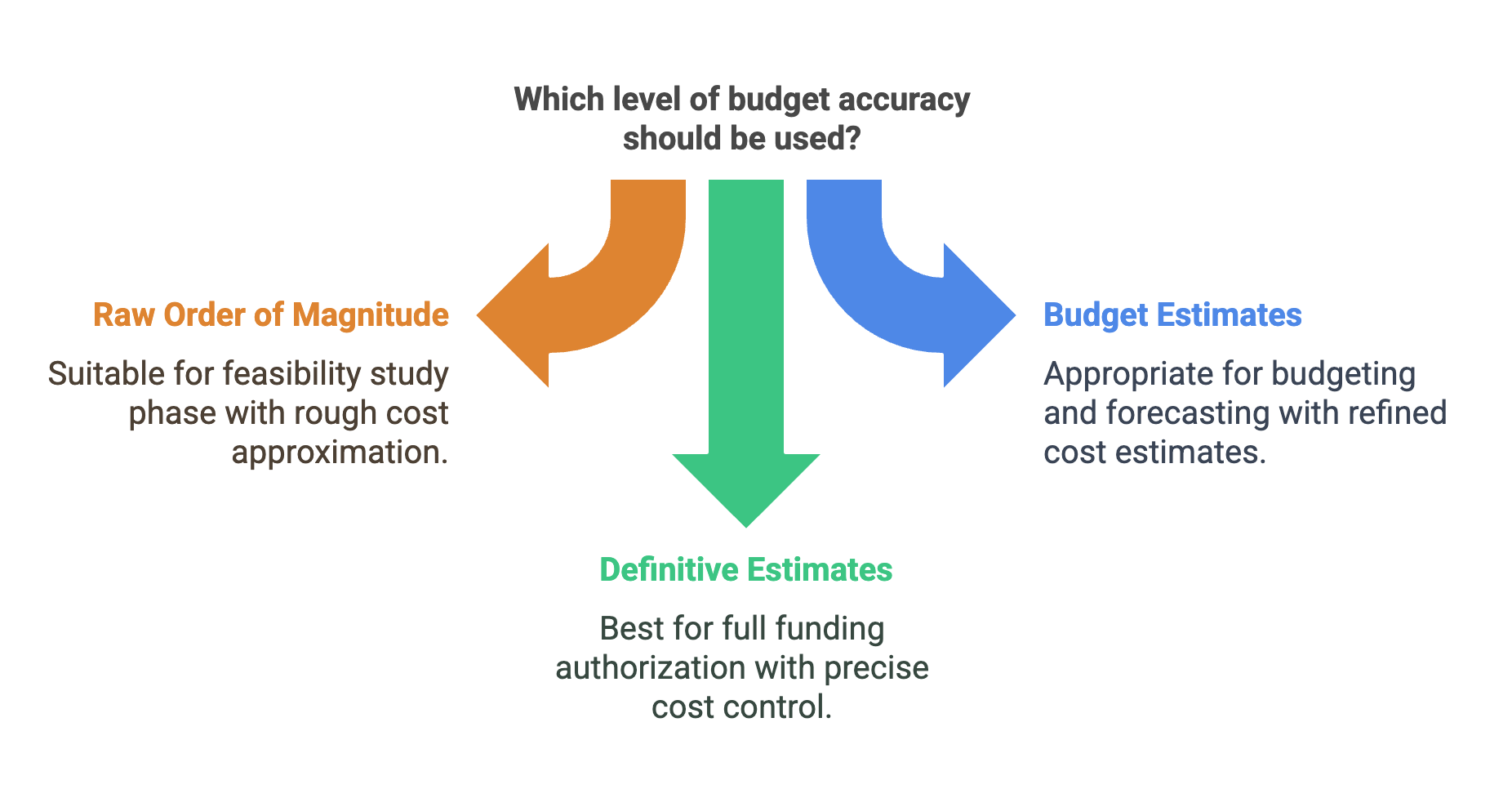
In summary, the accuracy of a project budget can vary significantly depending on the project phase and the information available. Using the appropriate level of budget accuracy at each stage helps in better financial planning, resource allocation, and overall project success.
Our Approach to Project Budget
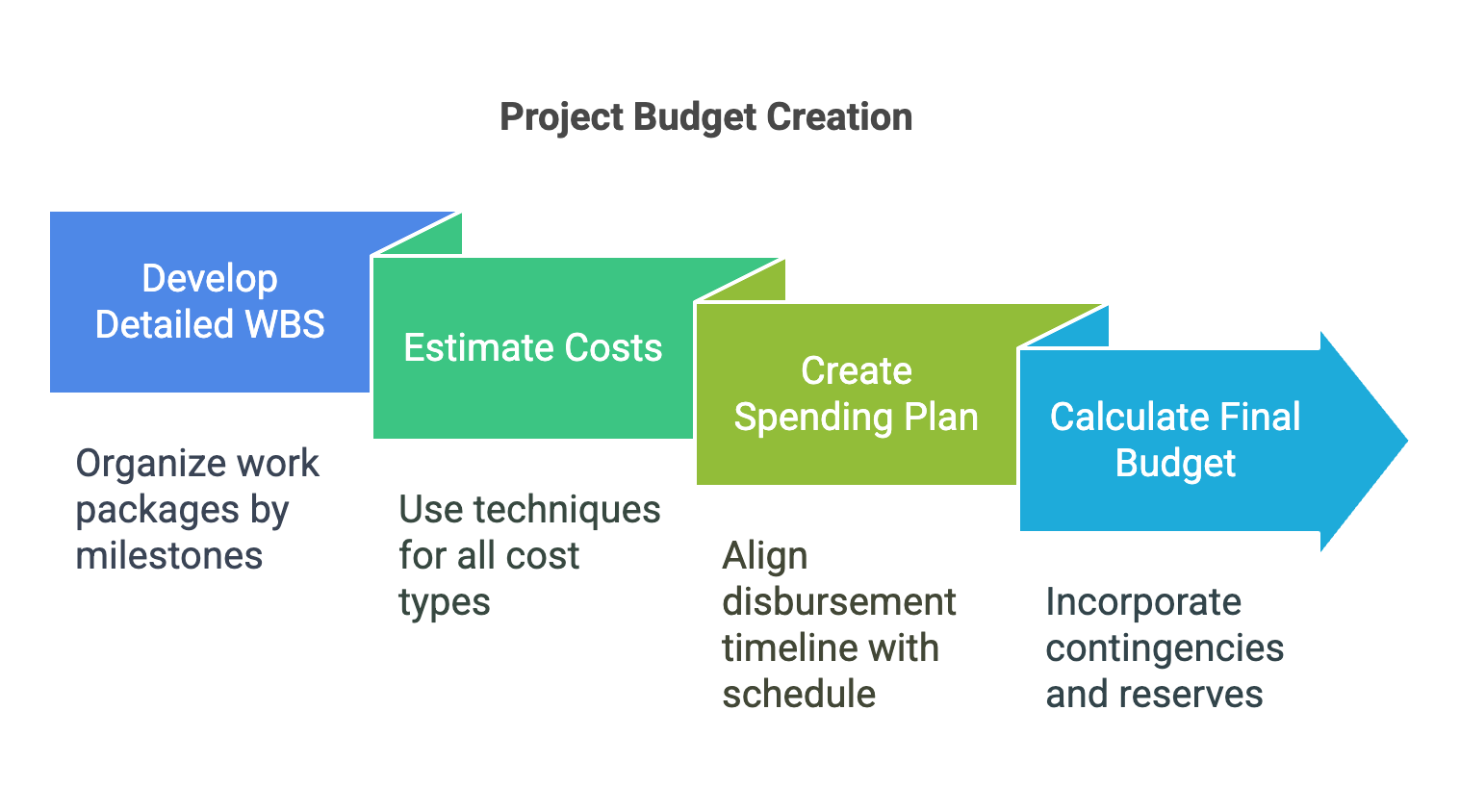
At Genialprojects, we advocate for a systematic approach to creating project budgets. Therefore, we suggest following these 4 easy steps to prepare a great one:
- Develop a Detailed WBS: Organize the main work packages by project milestones or deliverables.
- Estimate Costs for Each Work Package: Use appropriate estimation techniques based on the type of estimate being conducted (ROM, Budget, or Definitive), and consider all cost types (fixed, variable, direct, indirect, sunk).
- Create a Spending Plan:Develop a timeline for disbursements aligned with the project schedule.
- Calculate the Final Budget: Incorporate contingency and management reserves to form the comprehensive budget.
To streamline this process, we have developed a collaborative template that visually represents all budget components. This tool facilitates easier budget creation and management, ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned and informed.
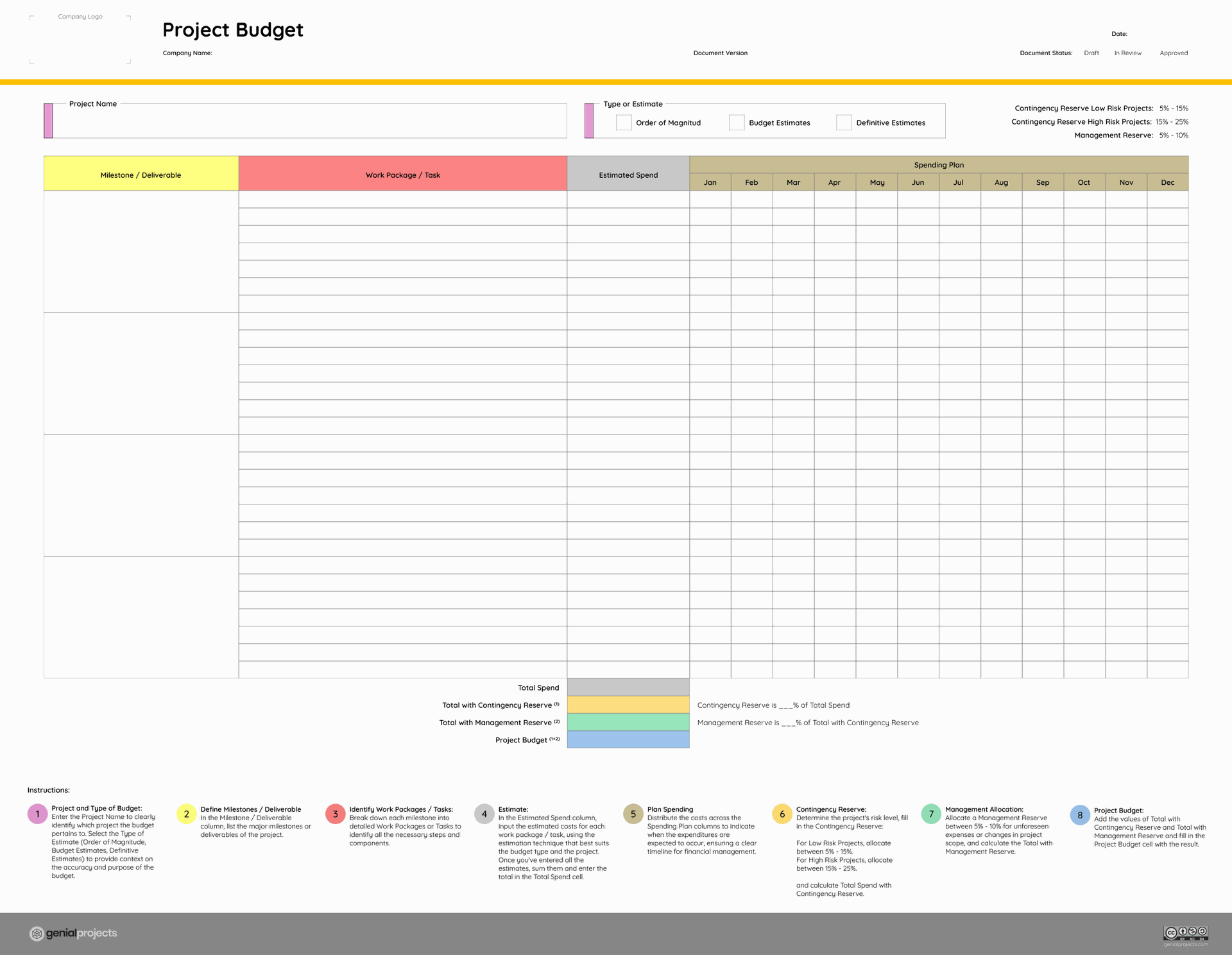
Free Project Budget Template available on our website.
Key Takeaways
Creating a project budget need not be a daunting task. By understanding the fundamental elements and following a structured approach, project managers can develop accurate and effective budgets that support project success. Key points to remember include:
- A project budget is an essential part of the Cost Management Plan and should be used throughout the project lifecycle for different reasons, from the feasibility study and project screening phases to controlling spending.
- Properly defined work packages and accurate cost estimation are critical to a reliable budget.
- Contingency and management reserves are necessary to manage risks and unforeseen expenses.
- Different cost estimation techniques should be used based on the project phase and required accuracy.
- Genialprojects provides a structured approach and collaborative tools to simplify the budgeting process.
By incorporating these practices, project managers can ensure financial control and project success, ultimately driving value for their organizations.