One of the key differentiators of successful projects is an effective risk management. Understanding the essence of risk within projects requires a holistic view, encompassing various facets that pose potential challenges or opportunities. This article delves deep into the expansive landscape of project risks, elucidating not only their definition but also the pivotal role they play in steering the course of a project's journey towards success or failure.
What Is Risk in Project Management?
Risk, within the context of project management, embodies the potential occurrence of an event that could impact the project's trajectory for better or for worse. It’s important to distinguish between risks and issues. An issue is a known or real problem that can affect the ability to complete a task. Risks, unlike issues, are unpredictable in their timing of occurrence, whereas issues can be anticipated.
Types of Risks
Project risks typically manifest in multifaceted forms, spanning across different realms. Internal risks, encompassing time, cost, and scope constraints, often originate within the project environment. For instance, a lack of experienced team members could pose a significant internal risk to project timelines and quality. Conversely, external risks stem from factors beyond the project's immediate control, potentially impacting its course. An example of an external risk could be a sudden regulatory change that affects project deliverables and schedules. Additionally, the concept of a "Single Point of Failure" highlights risks that, if realized, possess catastrophic potential, capable of halting project activities in their entirety. A critical software system that, if it fails, would halt the entire project workflow is a classic example of a single point of failure.
Understanding these classifications provides a foundational understanding essential for efficient risk management strategies.
The Role of the Project Manager Regarding Risks
Irrespective of the employed project management framework, the project manager assumes a pivotal role in addressing and managing risks. Their responsibility transcends merely overseeing project activities; it encompasses vigilantly monitoring, controlling, and strategizing to mitigate risks throughout the project lifecycle. The project manager acts as the linchpin, orchestrating risk management efforts to steer the project towards successful fruition.
Risks Throughout the Project Lifecycle
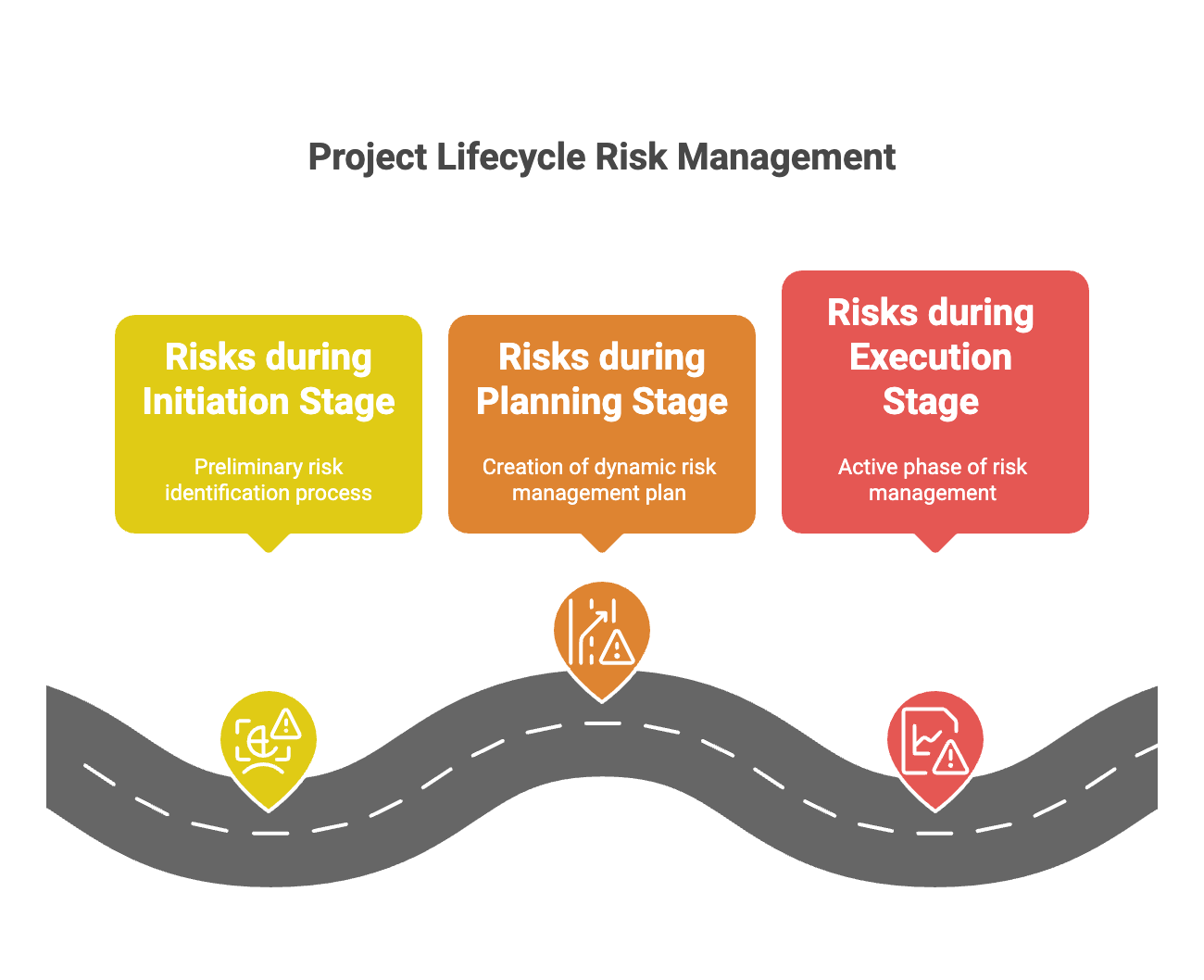
Risks during the Initiation Stage
At the project's inception, the project manager conducts a preliminary risk identification process. This involves compiling a list of potential risks that could influence the project's trajectory, an inclusion that could significantly impact decision-making processes, especially for risk-averse organizations.
Risks during the Planning Stage
The planning phase necessitates a comprehensive identification and planning strategy for risks. This phase culminates in the creation of a dynamic risk management plan, a living document encapsulating high-level risks and corresponding mitigation strategies.
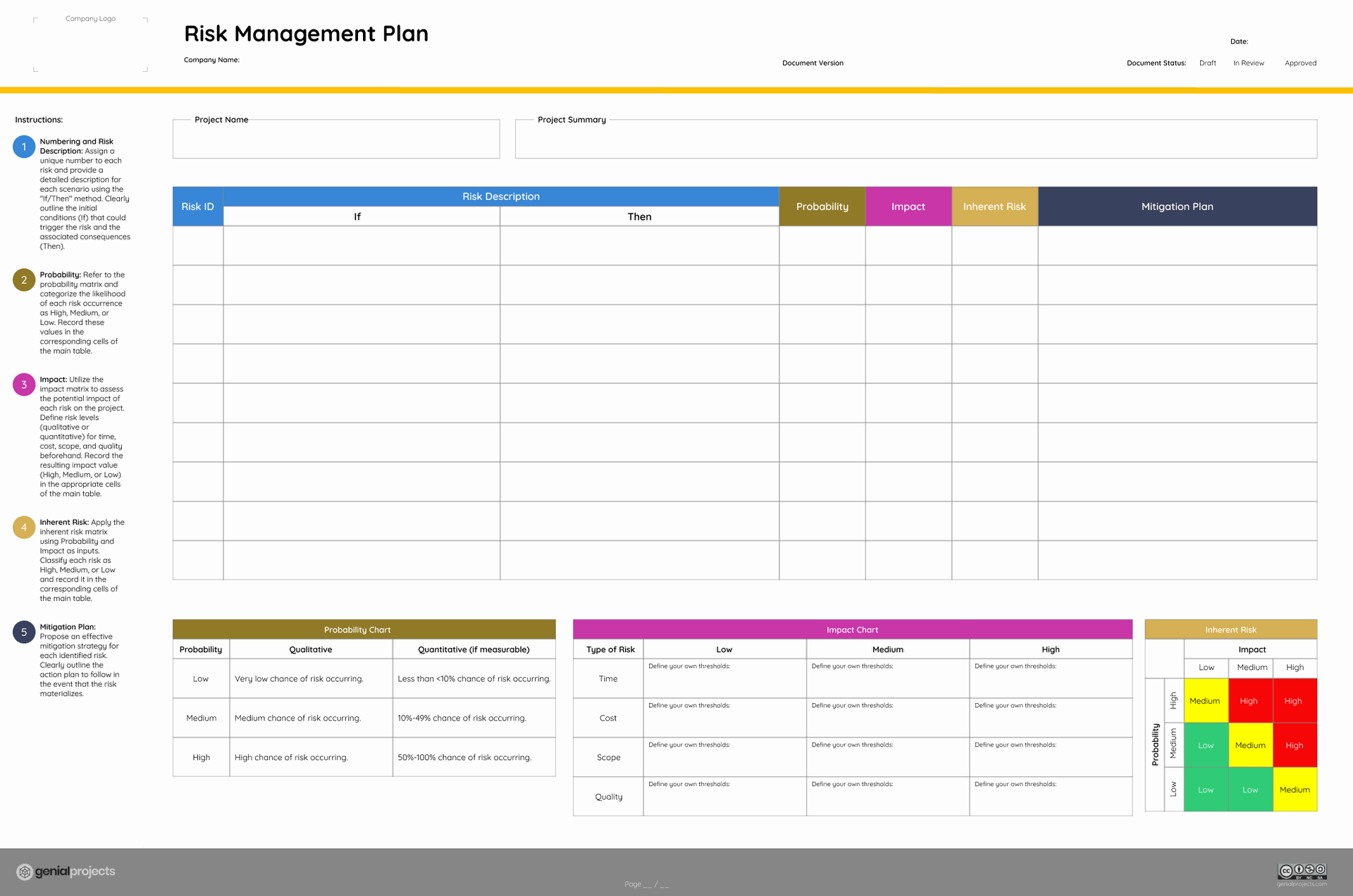
Free Risk Management Plan Template available on our website.
Risks during the Execution Stage
Execution marks the active phase of risk management. Here, the project manager employs various risk management techniques like Risk Exposure evaluation, ROAM analysis, and Escalation to continually monitor, evaluate, and respond to emerging risks.
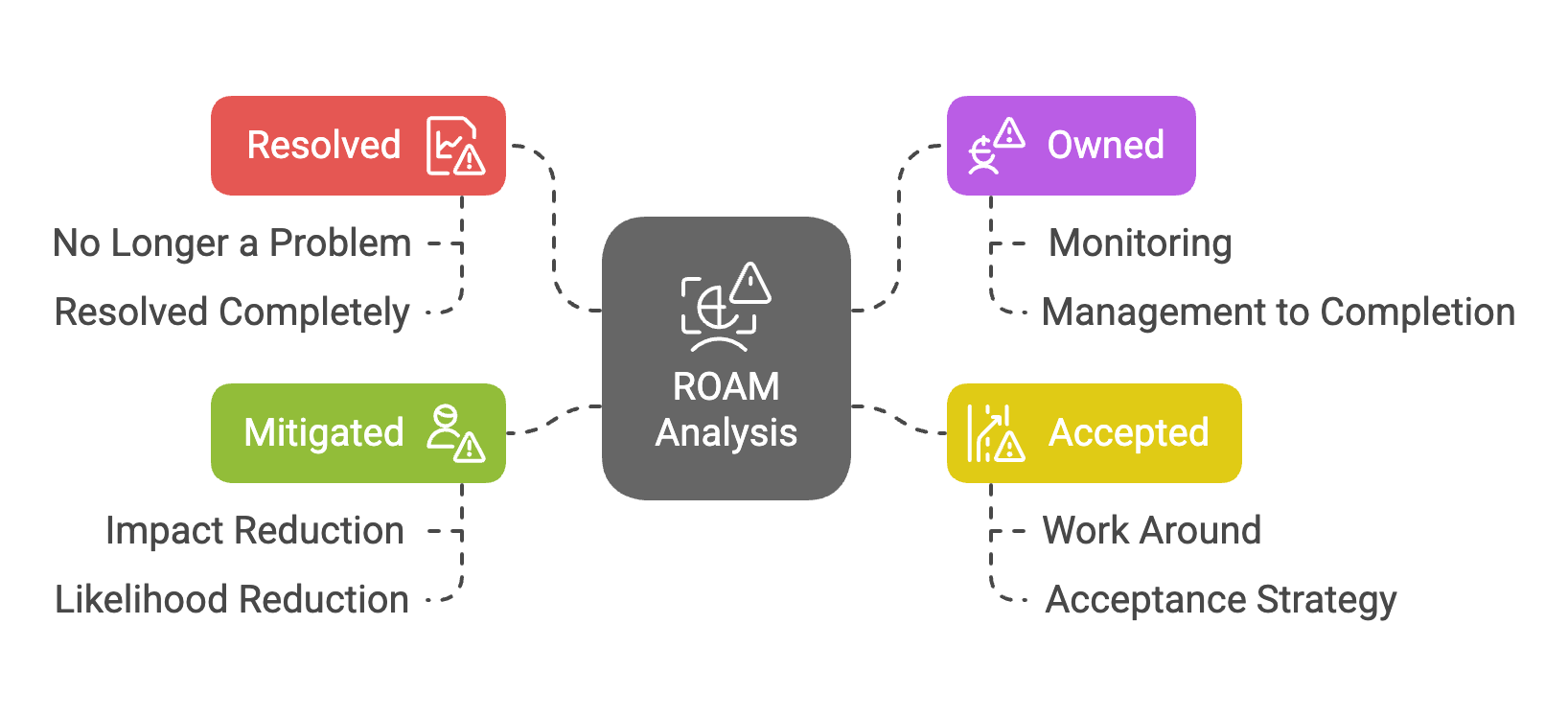
ROAM analysis offers a structured approach to help manage actions after risks arise and become issues. It categorizes risks into four key domains: Resolved, Owned, Accepted, and Mitigated. This method empowers project managers to swiftly assess risks and determine appropriate actions.
- Resolved: Risk has been resolved and no longer poses a problem.
- Owned: Risk that is assigned an owner responsible for monitoring and manage it through to completion.
- Accepted: Risk that cannot be resolved, so the team chooses to accept it and work around it.
- Mitigated: Risk for which proactive measures have been taken to reduce the impact (or reduce the likelihood of a risk that has not been materialized).
By employing the ROAM analysis, project managers can systematically navigate uncertainties, make informed decisions, and ensure the project progresses with minimized exposure to potential threats. This structured approach enhances adaptability and responsiveness, enabling teams to address emerging risks promptly and maintain project momentum towards successful delivery.
Free ROAM Analysis Template available on our website.
Identifying Risks
The process of identifying risks within a project necessitates an array of techniques and tools. Employing methodologies like brainstorming, cause-and-effect diagrams, and maintaining a risk register enables comprehensive identification, ensuring no potential risk goes unnoticed.
Cause and effect diagrams, also called fishbone diagrams, are visual tools used to map out potential causes contributing to a specific problem or risk within a project. Structured like a fish's skeleton, these diagrams categorize potential causes into branches stemming from a central issue. Categories such as people, processes, technology, environment, and policies are often used, allowing teams to systematically explore and analyze various factors influencing identified risks. This method facilitates structured brainstorming sessions, helping teams visualize and understand the complex interrelationships among different elements contributing to a risk.
Employing cause and effect diagrams enhances the depth of risk identification efforts by offering a systematic approach to dissecting potential causes. By visually organizing factors that might contribute to a risk, these diagrams enable teams to distinguish between root causes and symptoms. This approach not only aids in comprehensive risk assessment but also encourages a more targeted and effective risk management strategy by addressing underlying causes rather than surface-level manifestations.
Risk Assessment
In the realm of risk management, assessment plays a crucial role in estimating or measuring the attributes of a risk. One invaluable tool, the probability and impact matrix, facilitates risk quantification by assigning probabilities and potential impacts, culminating in the calculation of inherent risk, thereby aiding in prioritizing risk responses.
An impact matrix, often integrated with probability assessments, is a pivotal tool in risk evaluation and prioritization. This matrix assigns quantitative values to the likelihood of a risk occurring and its potential impact on project objectives or outcomes. It operates on a grid or matrix format, with likelihood typically plotted on one axis and impact on the other.
By mapping out the intersection of probability and impact, the impact matrix allows for the visualization and classification of risks based on their severity. Risks falling into high probability and high impact zones pose a significant threat and require immediate attention, while those in lower zones might necessitate different response strategies. This matrix aids in prioritizing risks, guiding the allocation of resources and efforts towards managing or mitigating the most critical risks that could potentially hinder project success. Its structured approach enhances decision-making by providing a clear framework for understanding the relative significance of different risks within a project context.
Risk Mitigation
Mitigating risks involves a strategic approach entailing the options to avoid, accept, reduce/control, or transfer risks. Within the domain of reducing or controlling risks, tools like Decision Trees aid in visualizing the broader impact of decisions on project outcomes, enhancing decision-making processes.
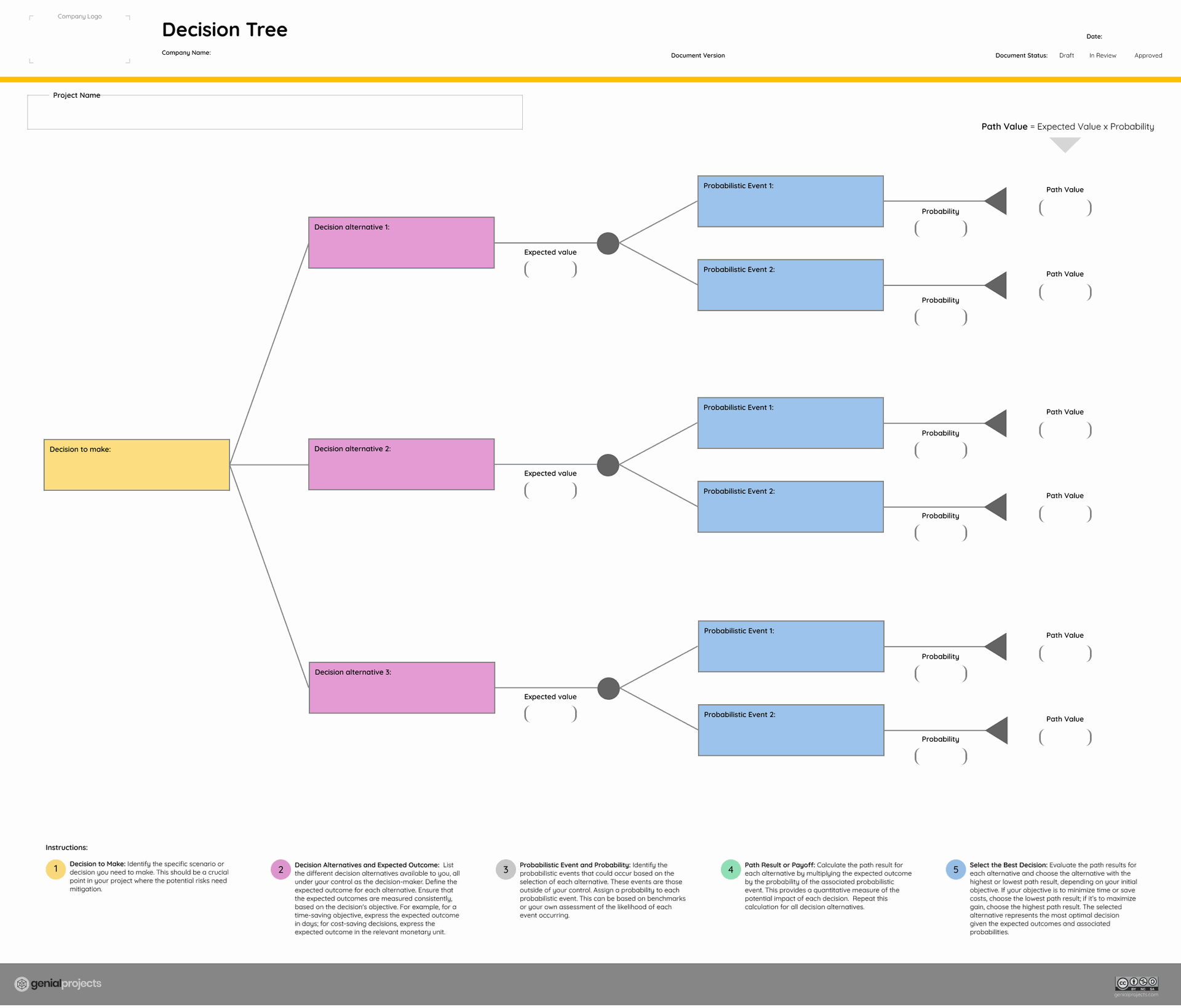
Decision trees serve as powerful tools in risk mitigation strategies, particularly in evaluating and visualizing the potential outcomes of various decisions in the face of uncertainty. They present a graphical representation resembling a tree, with nodes representing decision points, branches depicting different alternatives or choices, and leaves illustrating the potential consequences or outcomes.
These trees help project managers and teams analyze complex decision scenarios by systematically mapping out possible choices and their associated risks and rewards. By quantifying probabilities and assigning values to potential outcomes, decision trees aid in objectively assessing the expected value of different options. This facilitates informed decision-making by highlighting the potential consequences of each choice and allowing for a structured evaluation of risks associated with each decision path. Ultimately, decision trees offer a structured approach to navigating uncertainties, enabling project teams to identify optimal strategies for risk mitigation and make well-informed decisions to minimize potential negative impacts on project outcomes.
Free Decision Tree Template available on our website.
Key Takeaways
- Risks within projects encompass multifaceted dimensions, necessitating a comprehensive approach to identification, assessment, and mitigation.
- Project managers assume a central role in navigating through risks, ensuring proactive management and response strategies throughout the project lifecycle.