The ability to swiftly navigate design challenges can make or break a project's success. The Design Sprints aim to provide teams with a structured framework to tackle these obstacles head-on. Through a combination of rapid ideation, prototyping, and user testing, Design Sprints empower teams to iterate quickly and validate concepts with minimal time and resources. They offer a strategic advantage by compressing months of work into a matter of days.
In this article, we describe Design Sprints, uncovering their significance within the product development lifecycle and providing some strategies for seamless execution.
The Product Development Lifecycle
The product development lifecycle guides initiatives from conceptualization to commercialization, delineating the stages essential for bringing ideas to fruition. Beginning with the inception of a concept through brainstorming sessions and market analysis, the lifecycle progresses through Defining, Designing, Testing, and culminates in the product's Launch. Each phase represents a crucial juncture where decisions shape the trajectory of the initiative, underscoring the importance of strategic planning and execution. Amidst this journey fraught with uncertainties, Design Sprints emerge as a catalyst for progress, offering a streamlined approach to address design challenges.
Incorporating Design Sprints into the product development lifecycle injects agility and responsiveness into the process, enabling teams to pivot swiftly in response to evolving market dynamics and user feedback. By integrating Design Sprints strategically, organizations can accelerate time-to-market, minimize resource wastage, and foster a culture of innovation.
User-Centered Design
User-centered design lies at the heart of creating products and services that resonate with their intended audience, prioritizing the needs, preferences, and experiences of users throughout the design process. By adopting a human-centric approach, teams gain invaluable insights into user behavior, preferences, and pain points, informing the development of solutions that address genuine needs. Grounded in empathy and understanding, user-centered design transcends mere functionality, striving to create meaningful experiences that enrich users' lives. Within this paradigm, frameworks like Design Thinking provide a structured methodology to Empathize with users, Define problems, Ideate solutions, Prototype concepts, and Iterate based on feedback.
Central to the success of user-centered design is the relentless pursuit of empathy, as teams endeavor to immerse themselves in the lived experiences of their target audience. Through ethnographic research, user interviews, and usability testing, teams gain a nuanced understanding of user needs and behaviors, laying the foundation for informed decision-making.
What is a Design Sprint and When to Use It?
Born out of the intersection of Agile Project Management and Design Thinking, Design Sprints are intensive, time-boxed (usually 5) day workshops designed to compress months of work into a focused burst of activity. By bringing together cross-functional teams in a collaborative environment (in-person or virtual), Design Sprints foster creativity, alignment, and rapid iteration, paving the way for breakthrough solutions. When teams and organizations face critical design challenges during a project's lifecycle, Design Sprints offer a strategic toolkit for generating, prototyping, and validating ideas with speed.
To leverage the full potential of Design Sprints, teams must assess the suitability of the methodology in addressing the specific nuances of their design challenges. Complex problems with multiple potential solutions, requiring input from diverse stakeholders, and possessing a scope amenable to rapid iteration are ideal candidates for Design Sprints. Moreover, teams well-versed in Agile Project Management frameworks like Scrum and design methodologies like Design Thinking are primed to harness the power of Design Sprints effectively. By aligning organizational goals, team capabilities, and project requirements, teams can embark on a Design Sprint journey poised for success, driving innovation and delivering value to stakeholders.
Design Sprint Phases
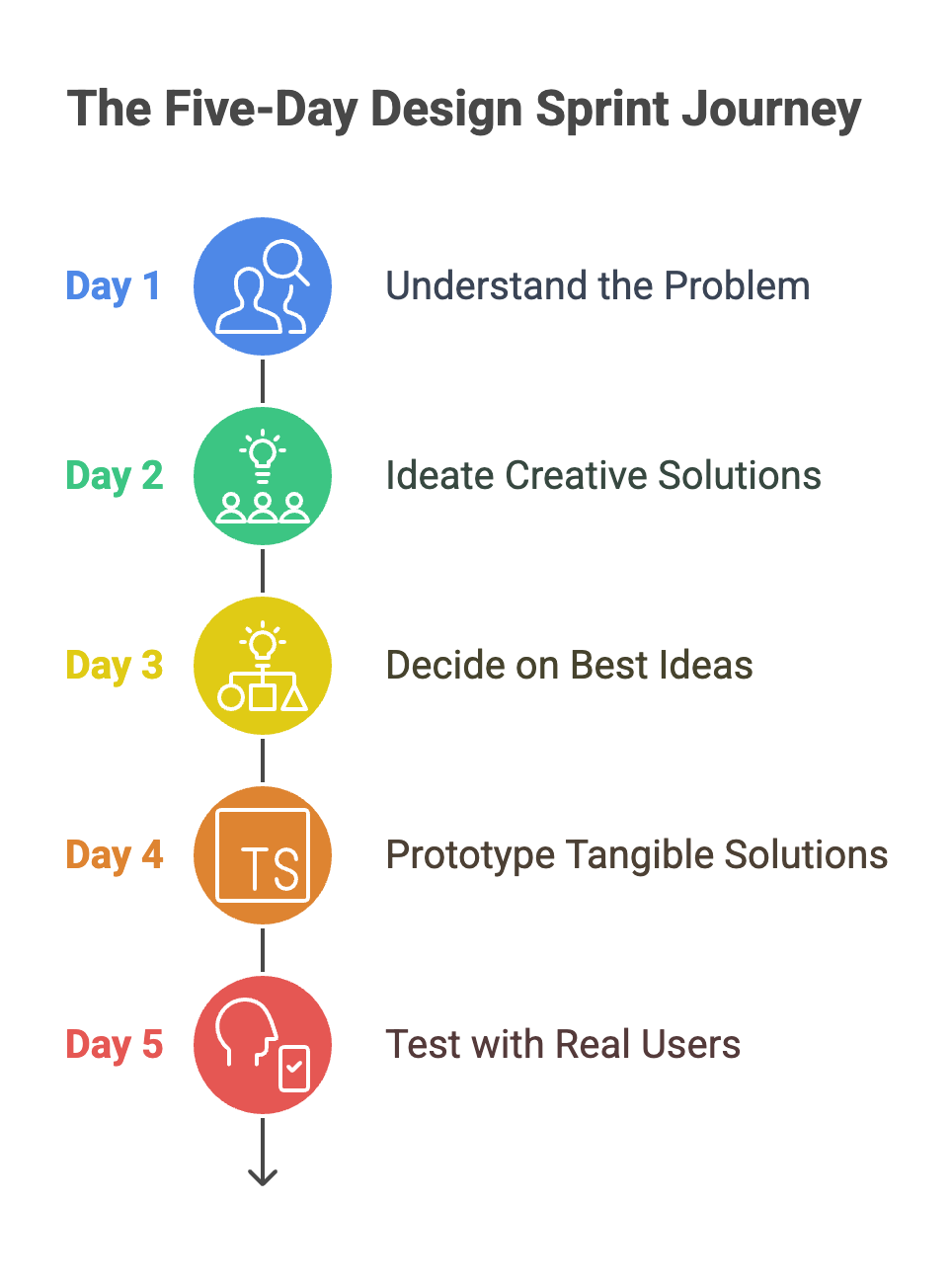
A design sprint consists of 5 phases: Understand, Ideate, Decide, Prototype, and Test. In the case that its duration is 5 days, each phase takes place over one day. Below is a description of the work carried out in each phase:
- Understand: This phase involves gaining a deep understanding of the problem at hand, often through user research and stakeholder interviews.
- Ideate: Here, teams generate a multitude of potential solutions, embracing creativity and lateral thinking.
- Decide: In this phase, teams evaluate and prioritize ideas, selecting those with the most promise for further development.
- Prototype: Teams transform selected ideas into tangible prototypes, allowing for quick iteration and refinement.
- Test: The final phase involves testing prototypes with real users, gathering feedback, and validating assumptions.
Planning a Design Sprint
Effective planning is essential for a successful Design Sprint. Key steps include conducting thorough user research, scheduling talks with experts to clarify the problem statement, securing an appropriate workspace, gathering necessary supplies, establishing ground rules, planning introductions for cross-functional teams, and outlining post-sprint actions for documentation and implementation.
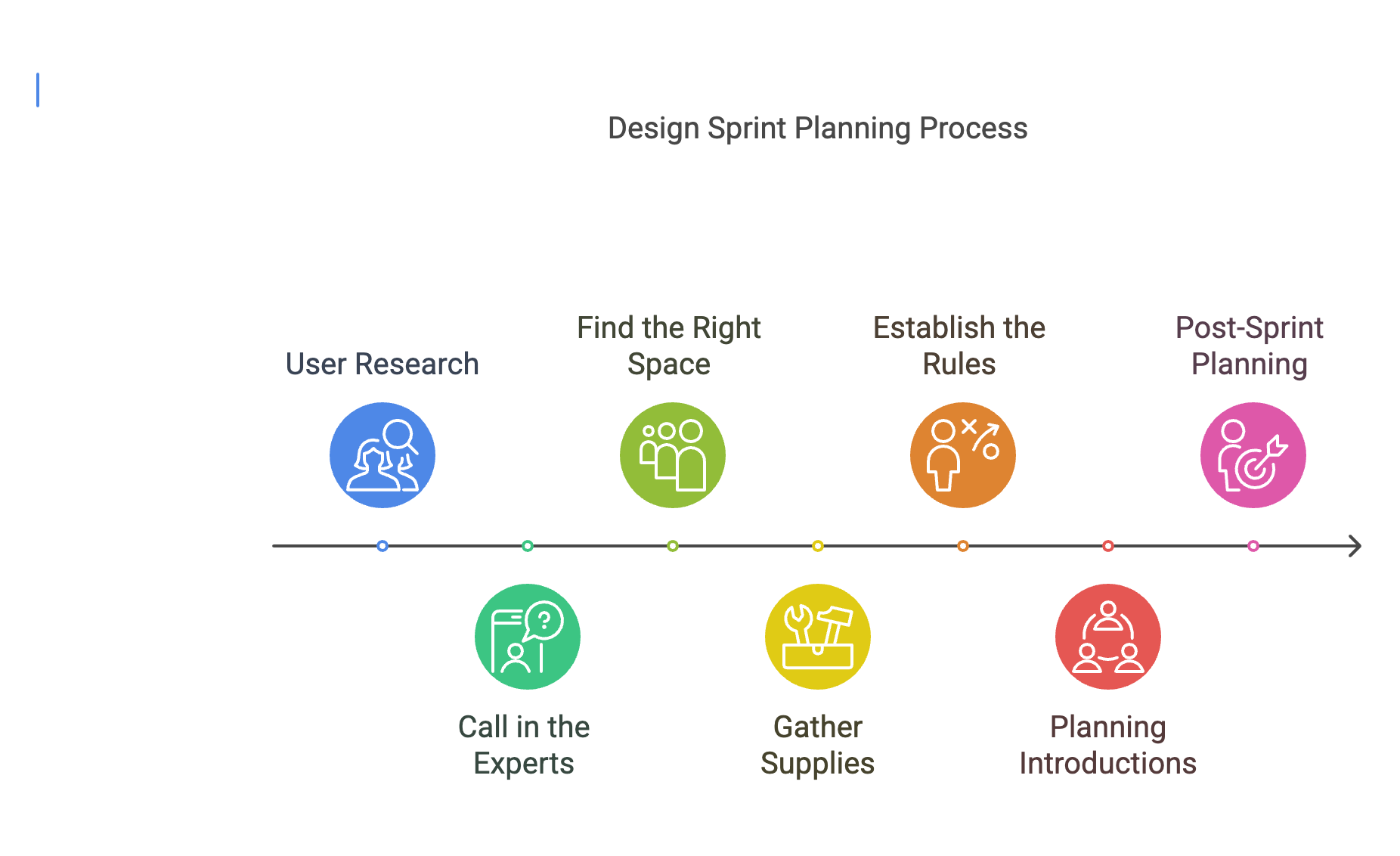
Proper planning is essential for ensuring the success and effectiveness of a Design Sprint. Follow these key steps to meticulously plan and execute your sprint:
Step 1 - User Research: Kick off your planning process by diving deep into user research. Identify and understand the specific problems or pain points your users are facing, which your sprint aims to address. This foundational research will guide the entire sprint process, ensuring that your solutions are truly user-centered and effective.
Step 2 - Call in the Experts: Schedule brief talks with relevant colleagues or industry experts to enrich your understanding of the problem space. These discussions serve to clarify the problem statement, gather diverse perspectives, and foster a shared understanding among team members. Leveraging the expertise of others can illuminate blind spots and inspire innovative solutions.
Step 3 - Find the Right Space: Selecting an appropriate workspace is crucial for facilitating collaboration and productivity during the sprint. Ensure that the chosen space accommodates the needs of all participants and provides an environment conducive to creative thinking and focused work. Whether it's a conference room, innovation lab, or virtual collaboration platform, prioritize inclusivity and accessibility.
Step 4 - Gather Supplies: Equip your team with the necessary tools and materials to support their activities throughout the sprint. Stock up on essentials such as markers, sticky notes, whiteboards, prototyping materials, and ample snacks and refreshments to fuel creativity and sustain energy levels. Providing a well-stocked toolkit sets the stage for productive ideation and rapid iteration.
Step 5 - Establish the Rules: Define clear ground rules and expectations upfront to streamline the sprint process and maintain focus. Establish guidelines for communication, decision-making, time management, and respectful collaboration. By setting a framework for interaction and workflow, you empower team members to contribute effectively and stay aligned with sprint objectives.
Step 6 - Planning Introductions: Given that Design Sprints often involve cross-functional teams with varying backgrounds and expertise, invest time in facilitating introductions and fostering team cohesion. Icebreaker activities, team-building exercises, or structured introductions can break down barriers, build rapport, and foster a sense of camaraderie. Cultivating a collaborative atmosphere enhances creativity and collective problem-solving.
Step 7 - Post-Sprint Planning: Anticipate what comes next by preparing for post-sprint activities and follow-up actions. Reflect on how the insights gained from the sprint can inform future initiatives or contribute to broader organizational goals. Document key learnings, decisions, and actionable insights to ensure continuity and accountability beyond the sprint. Effective post-sprint planning ensures that the momentum generated during the sprint is sustained and translated into tangible outcomes.
By meticulously planning each aspect of the Design Sprint process, from user research to post-sprint activities, teams can maximize the impact of their efforts and drive meaningful innovation. Embrace these steps as guiding principles to orchestrate a successful and transformative Design Sprint experience.
Retrospective Meeting in a Design Sprint
Immediately following a Design Sprint, teams should conduct a retrospective meeting to reflect on the process. This collaborative critique allows participants to highlight what went well and identify areas for improvement. By asking key questions such as what went well and what can be improved, teams gain valuable insights to inform future sprints and enhance overall effectiveness.
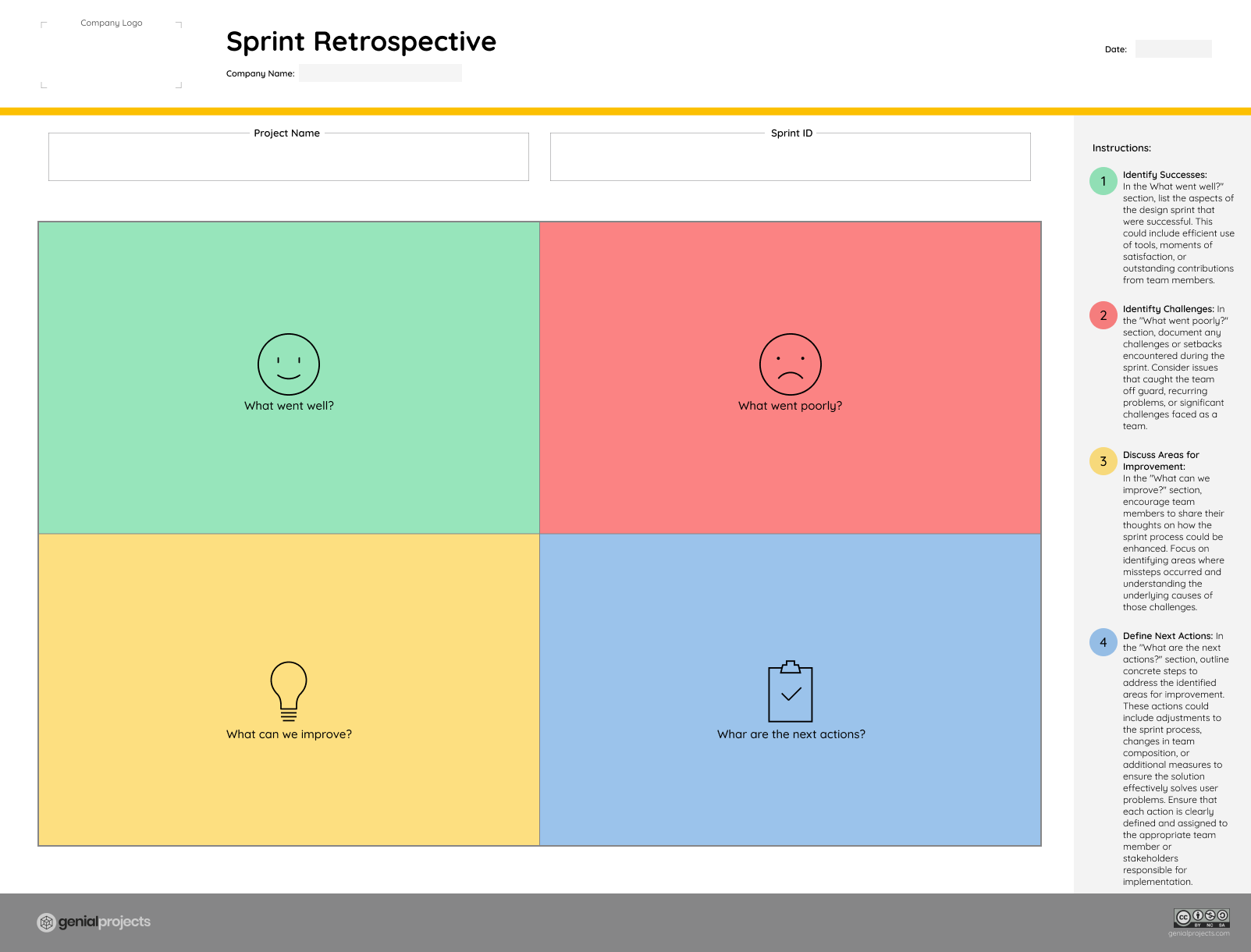
Free Sprint Retrospective Template available on our website.
Key Takeaways
- Design Sprints offer a structured approach to addressing complex design challenges swiftly.
- The principles of user-centered design form the basis of effective product development and are the foundation of Design Sprints
- Proper planning and execution are crucial for maximizing the benefits of Design Sprints.
- Retrospective meetings facilitate continuous improvement and learning within teams.
In conclusion, Design Sprints serve as a valuable tool for teams navigating the intricate landscape of product development, enabling them to innovate rapidly and deliver user-centric solutions effectively. By integrating Design Sprints into their workflow, organizations can foster a culture of creativity, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
With this comprehensive guide, project managers, product leaders, executives, entrepreneurs, and innovators are equipped to harness the power of Design Sprints to overcome design challenges and drive success in their initiatives.